The usage of BatchSEEnvironment in JBeret
The BatchSEEnvironment implements the BatchEnvironment interface and it’s used in Java SE environment if no container like WildFly is present. Here is the class diagram of the BatchSEEnvironment diagram:
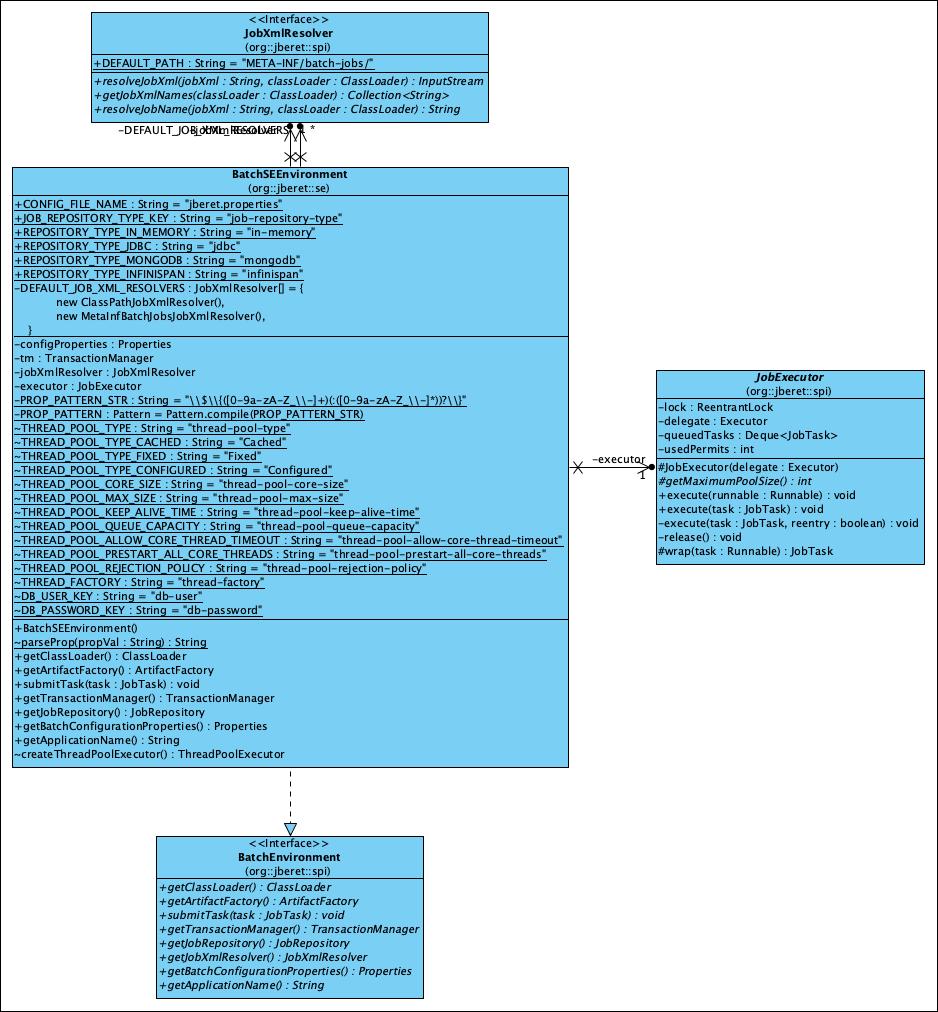
In the resources directory of the jberet-se module it contains the provider-configuration file:
➤ pwd
/Users/weli/works/jsr352/jberet-se/src/main/resources/META-INF/services
➤ ls
org.jberet.spi.BatchEnvironment
➤ cat org.jberet.spi.BatchEnvironment
org.jberet.se.BatchSEEnvironment
And in the JobOperatorImpl, in the run method, it will load the implementation of BatchEnvironemnt into runtime:
public class JobOperatorImpl extends AbstractJobOperator implements JobOperator {
private static final PrivilegedAction<BatchEnvironment> loaderAction = new PrivilegedAction<BatchEnvironment>() {
@Override
public BatchEnvironment run() {
final ServiceLoader<BatchEnvironment> serviceLoader = ServiceLoader.load(BatchEnvironment.class);
if (serviceLoader.iterator().hasNext()) {
return serviceLoader.iterator().next();
}
return null;
}
};
...
}
In addition, in jberet-core, it contains another provider-configuration file that defines the default JobOpeartor implementation:
./jberet-core/src/main/resources/META-INF/services/jakarta.batch.operations.JobOperator
Here is the content of the above file:
➤ cat ./jberet-core/src/main/resources/META-INF/services/jakarta.batch.operations.JobOperator
org.jberet.operations.DelegatingJobOperator
The DelegatingJobOperator will finally use the DefaultJobOperatorContextSelector to select the JobOperatorImpl during runtime:
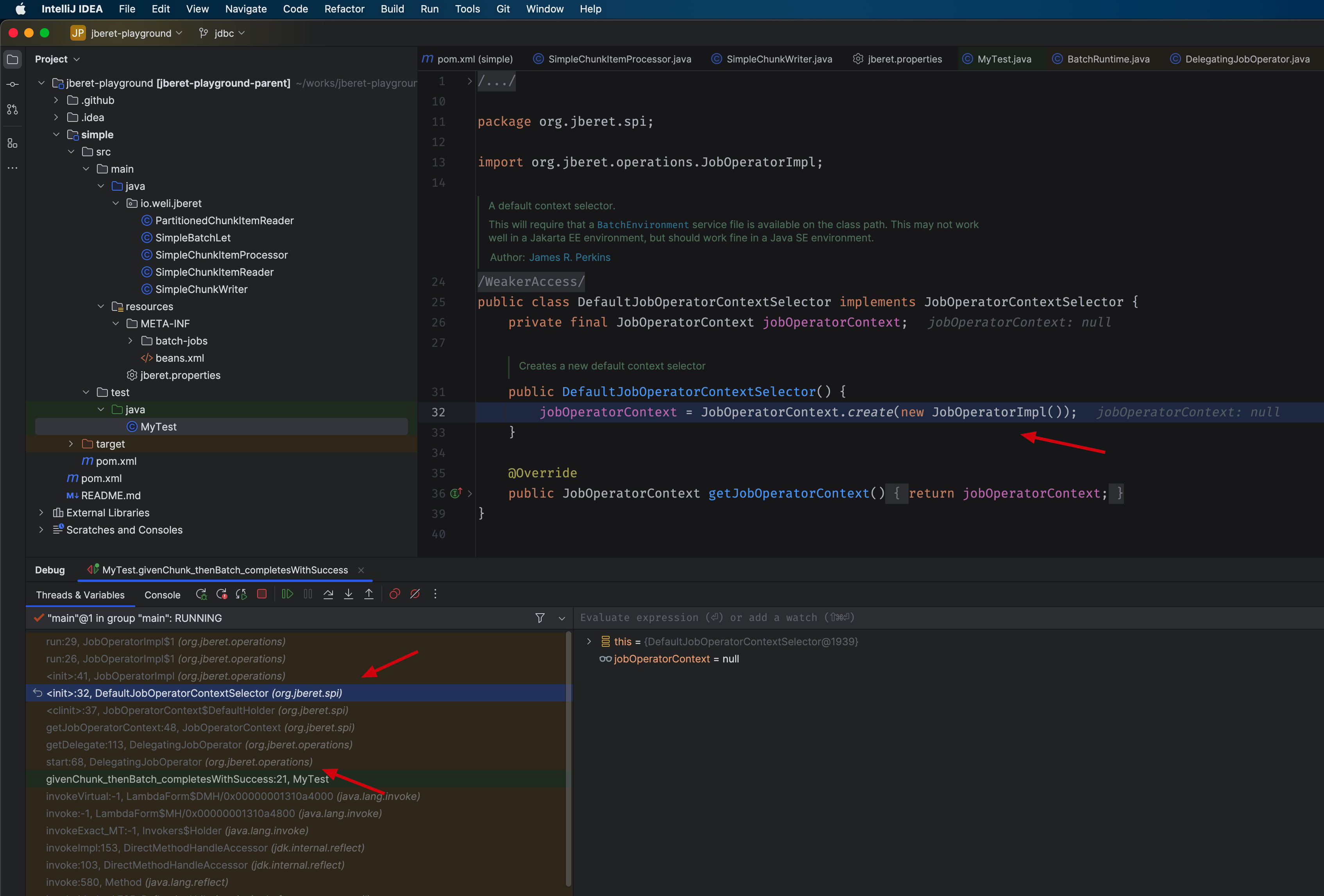
And finally the JopOperatorImpl will finally use the BatchSEEnvironment if it’s in the classpath. To show the usage of the BatchSEEnvironment, I have setup a project here:
To use BatchSEEnvironment, the jberet-se module must be present in the dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jberet</groupId>
<artifactId>jberet-se</artifactId>
</dependency>
And the service loader configuration file and the BatchSEEnvironment will be loaded during the runtime. In addition, the weld modules must be present so the @Inject and other CDI beans can be managed by the Weld container:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jboss.weld</groupId>
<artifactId>weld-core-impl</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jboss.weld.se</groupId>
<artifactId>weld-se-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
In addition the BatchSEEnvironment will read the settings from the jberet.properties file in the resources directory:
In the example project file, I have setup the job-repository to use JDBC type repository, which I’ll describe the usage of the JDBC repository in another blog post.